Spring-data + Mongo: Auto-increment sequence in MongoDB using a Spring service
Introduction
In this article, I'll show you how to assign an automatically incremented sequence value to a field using a Mongo collection. We'll use the same technique shown in the mongodb.com tutorial but with pure Java methods.
This procedure is useful when you need to assign public or easily rememberable identifiers for users (invoice numbers, supplier numbers, shipment numbers, etc.).
It's important to note that this value should not be used as the unique document identifier—MongoDB already provides better ways to assign document IDs, and using this approach is generally considered bad practice. Also, in distributed systems or databases with a huge number of documents, this methodology should be avoided.
Sequence collection
Just like in the MongoDB tutorial, we'll have a @Document for each sequence we use. This document will store the last value used for each sequence.
For example, in JSON notation:
{
"_id": "userid",
"seq": 0
}Let's create the following Java class:
@Document(collection = "sequences")
public class Sequence {
@Id
private String id;
private Long value;
//....//
}Next, we'll create a Spring service to safely get the next value for each sequence.
In the original tutorial, the following Javascript function is used:
function getNextSequence(name) {
var ret = db.counters.findAndModify(
{
query: { _id: name },
update: { $inc: { seq: 1 } },
new: true
}
);
return ret.seq;
}We'll add this logic to a Spring @Service that can be used when saving a document that needs a sequence value:
@Service
public class SequenceService {
@Autowired
private MongoOperations mongo;
//...//
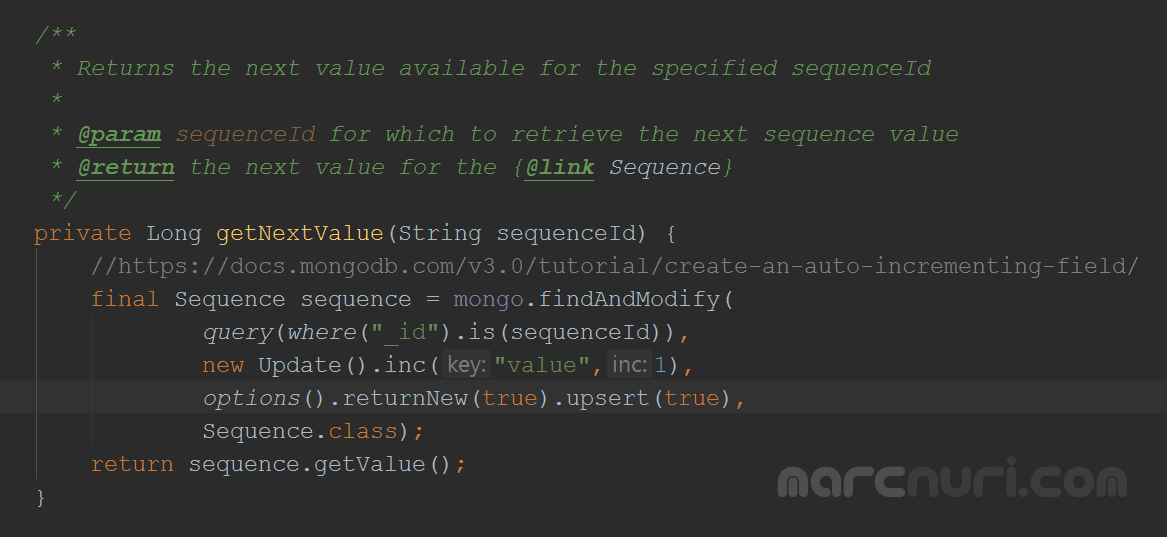
public Long getNextValue(String sequenceId) {
//https://docs.mongodb.com/v3.0/tutorial/create-an-auto-incrementing-field/
final Sequence sequence = mongo.findAndModify(
query(where("_id").is(sequenceId)),
new Update().inc("value",1),
options().returnNew(true).upsert(true),
Sequence.class);
return sequence.getValue();
}
}This function can then be used in another service or repository when saving a document (e.g. an invoice):
@Service
public InvoiceService {
@Autowired
private SequenceService sequenceService;
@Autowired
private InvoiceRepository invoiceRepository;
//...//
public Invoice insert(Invoice newInvoice) {
//...//
newInvoice.setPublicId(sequenceService.getNextValue("INV"));
//...//
return invoiceRepository.insert(newInvoice);
}
//...//
}The findAndModify function
The main function used is findAndModify(), which modifies and returns a single document. It's important to apply the function by filtering on a field that uniquely selects the sequence. In this case, we locate the sequence by "_id".
The code snippet new Update().inc("value",1) will increment the "value" field by one.
The returnNew(true) option makes the function return the new document instead of the original.
The upsert(true) option creates a new document if the specified sequence doesn't exist yet.
Download source code
You can find a sample project with the code shown in this tutorial, including a @RestController to retrieve sequence values and a unit test to verify correct generation and storage, at the following link:
