Running Apache Tomcat and Apache HTTPD on port 80 simultaneously
Apache Tomcat and the World Wide Web

Usually when running an application server, such as Apache Tomcat, you bind a connector directly on port 80. This way users visiting your web application will be able to navigate through your server just by calling your domain instead of calling your domain and special port (http://yourdomain.com:8080). If there is no option to bind a Tomcat connector on port 80 (some systems ban this functionality for security purposes), there are other ways to achieve this behavior such as setting a redirect on port 80 to port 8080 (Tomcat's default, or any other) using IPTables any other port redirection tool. Both options are really simple procedures, but are a great issue if you need to run a simple HTTP server on your machine too.
Apache HTTP and mod_proxy
To solve this problem we can run Apache HTTPD as a front-end proxy for Apache Tomcat and redirect traffic to the application server based on a set of rules. In this tutorial we will use mod_proxy, although there are many other options available.
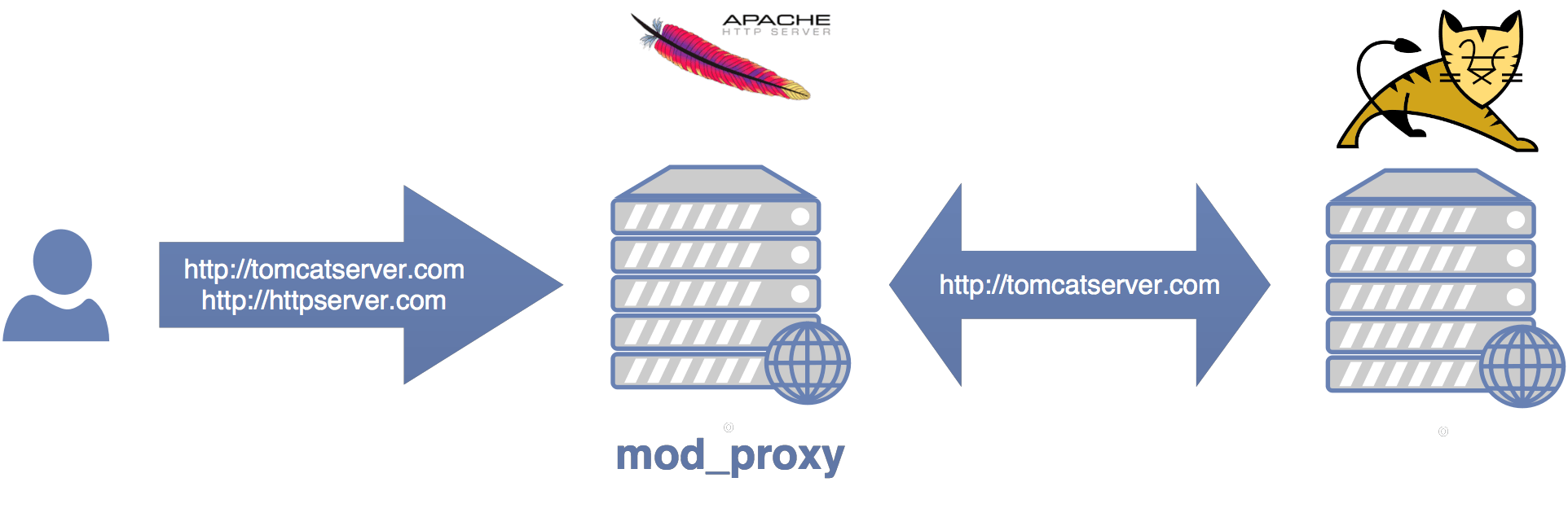
This tutorial assumes that Apache Tomcat is already installed and configured with the default connector settings (port 8080) and Apache HTTP is installed too with the default listener settings (port 80).
For this tutorial we are going to assume that there are 2 different domains (tomcatserver.com and httpserver.com) pointing to the same IP address. The user expects to reach the application server when navigating to one domain and the web server when navigating to the other.
First step is make sure that the file httpd.conf has mod_proxy enabled (which is by default), so in case it isn't, uncomment the following line.
LoadModule proxy_module modules/mod_proxy.so
Taking into account that there are 2 domains, we need to use the NameVirtualHost directive and define two virtual hosts based on the different domains.
NameVirtualHost *:80
Next, we define the virtual host that will redirect traffic to tomcat. In case tomcat has some virtual hosts defined too, we'll add a ServerAlias for each domain that needs to reach tomcat.
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin root@localhost
ServerName tomcatserver.com
ServerAlias tomcatserver1.com
ServerAlias tomcatserver2.com
DefaultType text/html
ProxyRequests off
ProxyPreserveHost On
ProxyPass / http://localhost:8080/
ProxyPassReverse / http://localhost:8080/
</VirtualHost>The DefaultType directive is used to set the default type for responses which don't specify it. This may happen with badly configured web applications and is something that Tomcat does by default and may arise bugs when using the proxified version.
ProxyRequests is a security measure, setting it to off will prevent your machine being used as a forward proxy server.
ProxyPass will map a remote server location to a local path. In this case, every request done to the root directory will be redirected to localhost at port 8080. Apache HTTP server will be simply mirroring the requests and responses from the client to the remote server.
ProxyReverse will adjust the headers from the remote server to match the locations expected by the client.
Next, we define the virtual host that will serve pages directly from Apache HTTP.
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin root@localhost
DocumentRoot /var/www/
ServerName httpserver.com
#Aliases
ServerAlias httpserver1.com
...
</VirtualHost>Proxy Rules
In this example we've assumed there are two different domains (or more) and that each domain will point to a different type of server. mod_proxy allows us to define more advanced rules, to proxy content based on other rules such as the context path.
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin root@localhost
DocumentRoot /var/www/
ServerName httpserver.com
#Aliases
ServerAlias httpserver1.com
ProxyPass /tomcat http://localhost:8080/
...
</VirtualHost>With this code, all traffic will be served by Apache HTTP, and only those requests to the '/tomcat' context path
will be proxied to Apache Tomcat. So http://httpserver.com/index.php will be served by Apache
HTTP and http://httpserver.com/tomcat/index.do will be served by Apache Tomcat.
