Fedora: How to install Cinnamon Desktop Environment complete guide
Looking for a more traditional desktop experience on your Fedora system? While GNOME offers a modern interface, many users prefer the familiar and customizable Cinnamon desktop environment.
In this comprehensive guide, I will walk you through installing and configuring Cinnamon on Fedora, transforming your system into a powerful, user-friendly workstation.
What is Cinnamon Desktop Environment?
Cinnamon is a free and open-source desktop environment originally derived from GNOME 3. It serves as the flagship desktop environment for Linux Mint and has gained popularity among users seeking a traditional desktop experience with modern functionality.
Why Choose Cinnamon Over GNOME?
While Fedora ships with GNOME as the default desktop environment, Cinnamon offers several compelling advantages:
- Traditional desktop layout: Familiar taskbar, system tray, and start menu.
- Highly customizable: Extensive theming and applet options.
- Resource efficient: Lower memory footprint compared to GNOME.
- User-friendly: Intuitive interface for Windows and macOS migrants.
- Stable and mature: Years of development and refinement.
Although you can download the official Cinnamon Spin of Fedora, installing it on your existing system gives you more control over the configuration and allows you to keep your current setup intact.
Prerequisites and System Requirements
Before installing Cinnamon on your Fedora system, ensure you meet the following requirements:
System Requirements
- Fedora Version: This guide works with Fedora 35 and newer versions
- RAM: Minimum 2GB (4GB+ recommended for optimal performance)
- Storage: At least 1GB free space for Cinnamon packages
- Graphics: Hardware with basic OpenGL support
Pre-Installation Checklist
-
Update your system to ensure compatibility:
sudo dnf update -y -
Check available space:
df -h / -
Verify DNF package groups are available:
dnf group list | grep -i cinnamon
Installing Cinnamon Desktop Environment
Let's get started with the installation process. Follow these steps carefully to ensure a smooth setup.
Step 1: Install Cinnamon Package Group
Open a terminal and run the following command to install all necessary Cinnamon packages:
sudo dnf groupinstall "Cinnamon Desktop"This command installs approximately 200+ packages including:
- Cinnamon desktop environment core.
- Essential applications (file manager, terminal, text editor).
- System settings and control panels.
- Multimedia codecs and fonts.
Step 2: Install Additional Recommended Packages
For a complete desktop experience, install these optional but recommended packages:
sudo dnf install cinnamon-settings-daemon cinnamon-screensaver lightdm lightdm-gtkStep 3: System Restart
After installation completes successfully, restart your system for changes to take effect:
sudo rebootTroubleshooting Installation Issues
If you encounter issues during installation, consider the following troubleshooting tips:
Problem: Package conflicts or dependency issues
# Clean DNF cache and retry
sudo dnf clean all
sudo dnf groupinstall "Cinnamon Desktop" --skip-brokenProblem: Insufficient disk space
# Check package download size before installing
dnf group info "Cinnamon Desktop"Problem: Installation interrupted
# Complete interrupted installation
sudo dnf distro-sync
sudo dnf groupinstall "Cinnamon Desktop"Selecting Cinnamon at Login
After rebooting, you'll need to select Cinnamon as your desktop environment:
- At the login screen, click on your username
- Look for the gear icon (⚙️) usually located near the password field
- Select "Cinnamon" from the session options
- Enter your password and log in
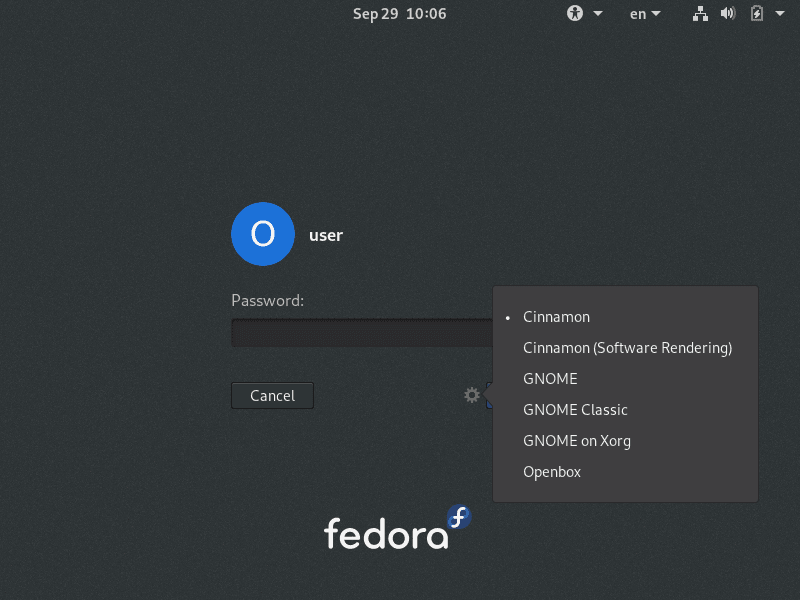
The previous image shows the login screen where you can select Cinnamon as the desktop environment.
Tip
Your desktop environment choice is remembered for future logins. You can always switch back to GNOME or other installed environments using the same method.
Post-Installation Configuration
Once you're logged into Cinnamon, I'd recommend performing some initial configuration to optimize your experience.
Configuring System Settings
Access the System Settings from the menu (usually bottom-left corner):
- Display: Configure resolution, scaling, and multiple monitors.
- Network: Set up Wi-Fi, VPN, and proxy settings.
- Power Management: Configure sleep, hibernate, and battery settings.
- Sound: Test audio output and configure input devices.
Installing Multimedia Codecs
Enable full multimedia support:
sudo dnf groupupdate multimedia --setopt="install_weak_deps=False" --exclude=PackageKit-gstreamer-plugin
sudo dnf groupupdate sound-and-videoCustomizing Your Cinnamon Desktop
Cinnamon is highly customizable. Following are some popular customization options:
Themes and Appearance
- Right-click on desktop → "Personalize"
- Browse available themes in "Themes" section
- Install additional themes:
sudo dnf install adapta-gtk-theme arc-theme numix-gtk-theme
Panel Configuration
- Right-click on panel → "Panel edit mode"
- Add/remove applets like system monitor, weather, or calendar
- Resize and reposition panels to your preference
- Configure panel auto-hide behavior
Keyboard Shortcuts
Access System Settings → Keyboard → Shortcuts to customize:
- Super + T: Open terminal
- Super + E: Open file manager
- Alt + F2: Run command dialog
- Ctrl + Alt + L: Lock screen
Performance Optimization
Memory and CPU Usage Comparison
Typical resource usage comparison on a 4GB RAM system:
| Desktop Environment | RAM Usage (Idle) | CPU Usage (Idle) | Boot Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cinnamon | 800-1200 MB | 1-3% | 25-35s |
| GNOME | 1200-1800 MB | 2-5% | 30-40s |
| KDE Plasma | 900-1400 MB | 2-4% | 28-38s |
Optimization Tips
-
Disable unnecessary startup applications:
- Open System Settings → Startup Applications
- Disable programs you don't need at boot
-
Configure graphics drivers (if using NVIDIA):
sudo dnf install akmod-nvidia xorg-x11-drv-nvidia-cuda -
Enable ZRAM for better memory management:
sudo dnf install zram-generator-defaults sudo systemctl daemon-reload sudo systemctl start systemd-zram-setup@zram0.service
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I switch back to GNOME?
Log out and select "GNOME" or "GNOME on Xorg" from the session menu at login screen. You can also remove Cinnamon completely:
sudo dnf groupremove "Cinnamon Desktop"Can I run both GNOME and Cinnamon simultaneously?
Yes! Both desktop environments can coexist. You can switch between them at login without conflicts. However, some system settings may be shared.
Cinnamon feels slow or laggy, what can I do?
Try these optimization steps:
- Disable compositing: System Settings → General → "Enable desktop compositing".
- Reduce visual effects: System Settings → Effects → Disable unnecessary effects.
- Check graphics drivers: Ensure proper drivers are installed for your GPU.
- Monitor resource usage: Use System Monitor to identify resource-heavy processes.
How do I install additional Cinnamon applets?
- Right-click on panel → "Add applets to panel".
- Click "Get more online" to browse community applets.
- Or installing via command line:
sudo dnf search cinnamon-applet
Can I use GNOME applications in Cinnamon?
Absolutely! GNOME applications work perfectly in Cinnamon. Popular GNOME apps like Nautilus, Gedit, and GNOME Terminal are often included by default.
Conclusion
Congratulations! You've successfully installed and configured Cinnamon desktop environment on your Fedora system. You now have access to a traditional, customizable, and efficient desktop experience that rivals any operating system.
Now that you've got Cinnamon up and running, don't forget to keep your system updated and in good shape. Follow the maintenance tips below to ensure a smooth experience.
Maintenance Tips
- Run
sudo dnf updateweekly to keep your system current - Regularly clean package cache:
sudo dnf clean all - Monitor system logs:
journalctl -p 3 -xbfor error checking - Backup your home directory before major system updates

